- IVF - In Vitro Fertilisation
- ICSI - Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection
- Tubal Recanalisation
- Ultrasound Guided Surgery
- Rent a Womb
- Artificial Insemination
IVF Treatment will depend on the cause of the infertility and the acceptability of the method by the couple. Discussion and counseling before implementation of decision.
- Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI) Injection of sperm into the uterine cavity. Done directly or under ultra sound guidance for the correct deposition of sperm to the fundal region, using the processed semen from husband / donor. Beneficial for women with unexplained infertility, poor cervical mucus & men with oligoastheno zoospermia. IUI is done in natural and stimulated cycles.
- Intra Cervical Insemination/Intra Vaginal Insemination (IVI)Injection of sperm into cervical canal of the uterus. Intra Cervical Insemination (ICI) is performed with donor semen in normal wives of Azoospermic husbands.
IVF & EMBRYO TRANSFER :
IVF includes union and fertilisation of sperm and egg in the laboratory outside the female pelvis; instead of inside the female pelvis in normal pregnancy. It involves controlled ovarian stimulation (COH), ultrasound guided ovum aspiration, insemination of ovum, incubation of gametes in CO2 incubator and transfer of embryos (ET) into uterus under ultrasound.
INVESTIGATIONS
- First stage:
At this stage, information is provided regarding the procedures, treatment plan and how the treatment plan is going to work. Required consent forms are signed. - Second stage:
The suppression of the pituitary gland Full suppression of the female ovaries using GnRH Agonists or GnRH antagonists. These medications as subcutaneous injections will prevent you from ovulating before the right time. Type and duration of suppression will depend on the previous medical history and present clinical status. The procedure starts from the 21 day of the previous cycle to 36 hours before OPU. - Third stage:
The stimulation of the ovaries and the monitoring of egg development The success of in vitro fertilisation treatment depends on the production of a multitude of eggs in the female ovaries. For this purpose, the ovaries which have been suppressed with the above-mentioned medications get stimulated with medications which stimulate egg development. These medications are injected subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
It takes approximately 10 Days for your ovaries to be stimulated through these medications. You have to be checked out a couple of times throughout this process for the monitoring of your egg development. During those checks ultrasonography will be performed and if deemed necessary the hormone levels in your blood will be checked to readjust the dosage of your medications. The duration is 10 -15 days from the day 2 (D2) of the period and ends with egg collection. - Fourth stage : Egg collection
During the monitoring of egg development, on the day it is determined that a sufficient number of eggs have matured, HCG (Human Chronic Gonadotropin) injection is carried out in order for the eggs to complete their final step of maturation, the collection of the eggs is scheduled for the 34-35 hours following this final medication injection.
You may be given a sedative or a medication to make you drowsy during egg collection. Alternatively, if you want the entire procedure may be performed under full anesthesia. The procedure is similar to the vaginal ultrasonography performed during your egg development follow ups. The only difference is the needle connected to the vaginal ultrasonography device which is inserted through the vagina to collect the eggs inside your ovaries.
The procedure lasts for an average of 30 minutes, then the Oocytes are inseminated with processed sperm from husband or donor. Fertilisation with sperm cells takes on the same day that the eggs are collected. - Fifth Stage : Laboratory Procedures
One day after the egg collection the couple is informed about the number of eggs fertilised normally following this stage the normally fertilised eggs are monitored under laboratory conditions for 2 to 5 days. When the time is right the most superior quality ones among them are carefully selected in certain numbers and placed back in the mother’s uterus. The couple gets informed on the timing of this Embryo transfer / blastoff transfer procedure. - Sixth stage : Embryo transfer
Prior to transfer procedure the couple is informed on the number and the quality of the embryos to be transferred. Transfer procedure is no different than a simple examination procedure. Anesthesia is optional.
The only requirement before the procedure is for the mother to drink a lot of water in order to fill up the bladder. The transfer procedure is performed under iconographic observation which requires the bladder to be partially full.
During transfer procedure a catheter loaded with embryos is passed through the vagina and the cervix and placed inside the uterus and the embryos are released inside the uterus. If there remains any superior quality embryos following the transfer consent is obtained from the couple to freeze and keep those embryo for future use.
Following the transfer the women is kept in the hospital for rest for 3-4 hours and later sent home. The woman is advised to spend the day resting in order to support the pregnancy. she will be started on hormones, once the eggs have been collected and the embryos have been transferred. The result of the treatment may be found out with the help of a pregnancy test 14 days after the transfer . If the result is positive an ultrasonically appointment is made to observe the heart rate of the baby within 3 weeks
INTRA CYTOPLASMIC SPERM INJECTION (ICSI)
ICSI is the injection of single sperm in to the ovum, thereby increasing the chances of fertilization and development of embryos. ICSI is done in conjunction with IVF- ET. ICSI is indicated in
- Fertilization failure in IVF
- Male Infertility
- Structural defects of Testis
- Unsuccessful Reversal Vasectomy
Sperm Used ( Extracted Sperm) :
The sperm used for ICSI may be taken either from masturbated semen or from extracted sperm. Testicular sperm extraction (TESE) / precutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration (PESA) /Micro Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (MESA) is performed by Fertility Surgeon for the purpose of extracting sperm for ICSI in severe anatomical defects in the male.
Donor programme – Third party reproduction (semen, ovum & embryo)
Semen, ovum and embryo donors are selected after adequate screening. For men with severe defects (Azoospermia & Aspermia). For women with ovarian failure in natural & stimulated cycles.
- Repeated poor quality ovum in IVF cycles
- Repeated fertilisation failure
- Upper age group (>40 years)
Surrogacy (Substitute Motherhood)
- For women with severe uterine abnormality
- Loss of children after hysterectomy
- Informed consent mandatory and appropriate counseling arranged.
High risk pregnancy
All ART /IVF pregnancy is considered high risk pregnancy, and all test tube babies are categorised as precious babies and taken care of accordingly. Outstation patients can return home after embryo transfer.
Facility at Mediwave IVF & Fertility Hospital
Assisted Reproductive Technology unit (ART – Test tube Baby procedure) Attached with HEPA filtered pressure module laminar flow air system laboratory and operation theatre (IVF, Lab & IVF OT). Our state of the art ART laboratory has all the modern facilities / equipments like Inverted Microscope with micro manipulator, sterio microscope, carbon dioxide incubators, laminar flow work benches, aspiration pump, embryo freezer unit etc.
TUBAL RECANALISATION
Infertility has become not only medical, but as well socio-economic problem. WHO has defined Infertility as lack of conception after at least 12 months of unprotected intercourse. About 15% of couples are infertile. In the female, many factors like cervical, uterine, tubal, ovarian, hormonal and pelvic causes contribute for the infertility. Out of these, tubal obstruction has been identified as the single most common cause for infertility.
HISTORY OF TR
TR is being done since 100 years with various kinds of methods. Some of the methods are –
- Macrosurgery
- Microsurgery
- Radiographic
- Sonographic
- Hysteroscopy
- Laparoscopy
- Combined OOH and SSG
HYSTEROSCOPY & SSG
- Hysteroscopic cannulation of the fallopian tube is safe diagnostic procedure that can be used to treat those patients with true proximal occlusion. (Deaton J.L).
- SSG with contrast media in detecting the tubal patency has also been shown to be comparable to HSG and Laparoscopy. ( Salata et al.,)
ADVANTAGES
- Combined SSG and OOH is less invasive and economical and does not require general anesthesia and hospitalization.
- It can avoid Laparoscopy. It will save time, money and inconveniences to the patient.
- It can avoid I.V.F
TECHNIQUES
- Cervical Dilatation under intravenous sedation and / or local cervical block.
- Tubal canulisation using Catheter and Guide wire under hysteroscopic guidance
- Agitated Saline and Antibiotic injections into the uterus under TVS vision.
- SSG to study the tubal patency after recanulisation.
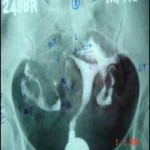
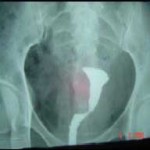
ORMAL H.S.G.
UT = Uterus, R.T + Right tube. L.T + left tube.
1 = Proximal.
2 = Middle.
3 = Distal portion.
4 = Peritoneal spillage of the dye.
BILATERAL PROXIMAL TUBAL BLOCK
Both the tubes are not filled with the dye. No peritoneal spillage of the dye is seen in the pelvis.
STEROSCOPY
Steroscopic Equipments:
- From top – Guide wire, Camera cable, Light cable, Outer sheath
- Operator sheath and TelescopeHYSTEROSCOPY
Hysteroscopic equipments:
- Top: Fibreoptic Light Source
- Bottom: Camera processor.
ACCESSORIES
- Normal saline two liter collapsible Plastic bottles
- Infusion set
- Foley’s catheter number 8
SSG PROCEDURE
SSG has been established as a safer, cheaper and easier technique to perform than HSG in the assessment of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. Several materials have been use as contrast media for studying tubal patency through transvaginal sonography Some of them are
v Saline
v Saline & air
v Echovist
LIMITATIONS OF SALINE
- Saline is a safe contrast media, its visibility is low.
- Sensitivity and specificity of for evaluation of the uterine cavity is 100 and 88.8%, respectively.
- Negative predictive value is 100%
- Positive predictive value is 97%.
- Sensitivity and specificity of the method for the assessment of the tubal status is 100 and 66%, respectively.
- Negative predictive value is 100% and positive predictive value is 61%.
LIMITATIONS OF SALINE & AIR
Saline & air do make a good contrast.
- The results were very similar to those of HSG, but differed in about 10% of the cases from those of laparoscopy.
- Studies have revealed that the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values were respectively 80, 85, 82.7, 85 and 80%.
- It is quit difficult to get a uniform mixture of saline and air even by repeated flushing with syringe. The air bubbles disappear quickly. Also the bubbles formed are not fine once.
ECHOVIST
- Echovist is quite expensive.
- For the assessment of tubal patency using positive contrast. Echovist the method has shown 100% sensitivity and negative predictive value of 77%
- Positive predictive value of 70%.
- There were no evident complications reported during or after the procedure.
Povidone – Iodine & Air as a new contrast medium.
- To over come above problem RESEARCH WAS DONE TO FOR finding out an ideal, low cost contrast media for SSG.
- SSG was performed using Povidone-Iodine Air solution as contrast media. Further status of the tubes was assessed by the “gold standards”, laparoscopy
Povidone – Iodine
- Povidone-Iodine is a safe antiseptic solution, which consists of Povidone-Iodine IP 5% w/v (Available Iodine 0.5% w/v).
- It is easily available and cheap. Surgeons have used it both outside the body and inside the body as antiseptic solution.
- Hence it has been established as safe antiseptic solution.
Povidone – Iodine and Air
- Povidone – Iodine when mixed with saline (Dilution done:1ml Povidone-Iodine + 20 ml Saline was used) and agitated with air filled syringe giving us an excellent frothy solution of Povidone-Iodine Air.
- The size of the bubble is quite small, uniform and long lasting. This can be used as an excellent contrast media for the study of fallopian tubes.
RESULTS 1
- The tube visualization is quit satisfactory.
- The Uterine cavity visualization is very good and Predicting the spillage into peritorial cavity is very good.
- It is excellent with Doppler studies.
- Sensitivity and specificity of the method for the assessment of the tubal status was 100% and 80% respectively. Negative predictive value was 100% and positive predictive value was 72%.
RESULTS of OOH and SSG
The results are better than the available meta analysis results achieved by other workers using techniques like macrosurgery, microsurgery, hysteroscopy and sonography separately.
CONCLUSIONS
Combined OOH and SSG is more effective at establishing and confirming tubal recanulisation and thereby achieving pregnancy. It appears to be less invasive, less costly and time saving than the other presently available techniques.
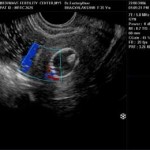
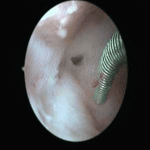
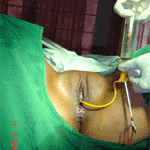
Ultrasound Guided Surgery In Treatment of Infertility
Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVS) now also offers infertile patients newer treatment options not available before. Modern surgical techniques have progressively become less and less invasive – all to the patient’s benefit. From laparotomy to laparoscopy, and now to ultrasound guided surgery, we are witnessing a change in the infertility surgeon’s armamentarium from the knife to the endoscope to the guided needle.
The benefits of “US guided surgery” are many and include: reduced costs; reduced hospitalization; reduced risk of complications; and better preservation of fertility, with increased chance of conception for the future. USG can be used both in the treatment of infertility as well as in the manufacture of the complication of the treatment of infertility.
Ultrasound-Guided Surgery
- Egg pickup for IVF – The use of vaginal ultrasound for egg pickup has made egg retrieval a short, simple and inexpensive procedure, which can be performed in a day-care unit, under sedation and local anesthesia. The ovaries are normally present in the pouch of Douglas, and are very accessible transvaginally. Moreover, the presence of adhesions does not interfere with egg collection.
- Ovarian cyst aspiration (Follicular Cyst)- An ovarian cyst is a very common condition in which fluid collects in the ovary. However, cysts which are more than 5 cm in size need to be treated, as they can cause problems ( eg twisting rupture). Normally, cystectomy is done and often this damages the surrounding normal ovarian tissue as well. With ultrasound-guidance, a needle is passed through the vagina into the cyst, and drain the contents ( usually serous fluid ) completely which often does not recur.
- Chocolate cyst aspiration- A Chocolate cyst is a very common condition in which thick endometriotic fluid collects in the ovary. Normally, surgery had to be done to remove these cysts – and often this damaged the surrounding normal ovary as well. With ultrasound-guidance, we can insert a needle through the vagina into the cyst, and empty the contents by sucking it out. We can inject sclerosing material to prevent reoccurrence.
- Ultrasound-guided embryo transfer for IVF- Techniques have been devised to pass a catheter set into the uterus through the vagina under ultrasound guidance, so as to place the embryos in the uterine cavity.
- Ultrasound-guided tubal gamete transfer for GIFT techniques-Techniques have been devised to pass a catheter set – into the fallopian tubes through the vagina under ultrasound guidance, so as to place the gametes in the fallopian tube.
- Tubal recanalisation for cornual blocks (proximal tubal obstruction) – Often cornual blocks are due to the presence of mucus plugs and amorphous debris in the tubal lumen /Ostia. Ultrasound guided tubal catheterization can effectively treat the blocked tubes in some patients.
- Tubo ovarian mass aspiration- A Tubo ovarian mass is a very common condition in which fluid collects in the tube and ovary. Normally, surgery had to be done to remove these mass – and often this damaged the surrounding normal structures. With TV ultraSound-guidance, we can insert a needle into the mass, and empty the contents by sucking it out.
- Hydrosalpinges aspiration- Hydrosalpinges is a common condition in which toxic fluid collects in the tube. Normally, surgery had to be done to excise these mass. With TV ultrasound-guidance, we can insert a needle into the dilated tubes, and aspirate the contents by sucking it out, & flush the tubes by injecting antibiotics to prevent reoccurance.
- PCOD Drilling- A study has been done by Ramzy A.M.1 et al on Transvaginal ultrasound guided ovarian stroma hydro coagulation in an office setting seems to be a safe, economic and practical procedure that is acceptable by the patients. If larger studies confirm its effectiveness it may be an attractive alternative to conventional ovarian drilling.
- Drainage of pelvic abscess: Collection of Pus in the Pelvic Peritonium cavity, pouch of douglash, can be drained through a cyst aspiratic needle using Ultrasound guidance
- Blood Cells – Ultrasound guided uterine surgeries: Polypectomy, D &C, Removal of Foreign bodies, MTB, Biopsy.
- Paracentesis – is a procedure in which a needle is inserted through the abdominal wall into the peritoneal cavity to obtain a simple of any fluid that is present. Sonography help the doctor guide the needle in to the abdomen.
Management of complication in Infertility treatments
Ultrasound guided surgery can be used to treat several complication that may arise while treating an infertile lady. Some of them are:
- Treatment of OHSS- Ascetic fluid aspiration. Ascetic fluid collection is a common condition in which large quantity of fluid collects in the peritoneal cavity when the ovaries are over stimulated (OHSS). With ultrasound-guidance, we can drain the fluid.
- Treatment of ectopic pregnancy- With technological advances (ultrasound and beta-HCG blood tests) the diagnosis of tubal pregnancy can be made very early, usually before rupture. It can be treated by injecting a toxic chemical, methotrexate, into the sac, which causes the tissue to die and then get reabsorbed, without any surgery whatsoever. In more advanced tubal pregnancies, potassium chloride can be injected direct into the heart of the foetus in the ectopic gestational sac, thus killing it and preventing in further complication.
- Multiple pregnancy Reduction: The Transvaginal ultrasound-guided technique is a feasible option for the management and preventionof the medical and obstetric risks associated with high-order multiple pregnancy resulting from assisted reproduction treatment. Embryo reduction should be carried out between the eighth and ninth week of pregnancy, using the technique described in this study.Ideally, one should attempt to reduce multiple pregnancy to twins or singleton.
The scope of ultrasound guided procedures has increased dramatically in the last few years; and with further improvements in technology, we can expect this list to become even longer, and doctors become more versatile with using this technology.
RENT A WOMB !!!
In today’s world 10-15% of married couples are unable to have children normally like others have. Intensive research in the field of reproductive medicine has led to the invention of several artificial techniques for having children. Some of these include Artificial insemination, In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT), etc. Surrogacy is one such technique of artificial reproduction.
Surrogacy means renting a womb of a mother for pregnancy. It’s an arrangement where one women (surrogate mother) agrees to bear a child for another women or a couple (intended parents) and surrender after it’s birth.
Who hires Surrogate mothers?
- A woman who is infertile or having problems like absent or poor functioning of Ovaries, absent or malformed Uterus, maternal disease which comes in the way of pregnancy, those having troubled pregnancy or repeated IVF failures may hire another woman to bear a child.
- Sometimes single man may also hire a woman to carry the child using his own sperm.
- Couples with infertile male partner.
Types of Surrogacy
There are two types of surrogacy:
- Traditional surrogacy: In this type, the surrogate mother not only gives her womb on hire but also donates her egg. She becomes the genetic mother of the child. The surrogate mother is artificially inseminated using semen. Semen may be taken either from the intended father or from the donor.
- Gestational surrogacy: In this type, the surrogate mother only gives her womb on hire and she is not the genetic mother. In this technique a fertilized egg is transferred to the uterus of surrogate mother. The egg used for fertilization may be taken from the intended mother or the donor & the sperm may be taken from the intended father or donor.
Eligibility for becoming a surrogate mother.
- A surrogate must be between the age of 18-35 & preferably should have her own child.
- She must be in good overall mental & physical health & be able to undergo pregnancy with minimum risk to her health.
- Overweight, heavy smokers, alcoholics, drug addicts are not suitable for surrogacy.
- She should have good support from all her family members especially her husband & children.
Problems faced by a surrogate
Certain health problems can arise like: gestational diabetes, high blood pressure, urinary-tract infections, haemorrage, painful intercourse, haemorrhoids & post-natal depression. In very rare cases pregnancy can result in maternal death. She may feel a great sense of loss due to separation from the child she gave birth to also her husband & children may feel the same. If a surrogate’s partner or families oppose her decision of being a surrogate then she may feel lonely & mentally upset.
Problems faced by intended parents
Their family members may find it difficult to accept the child & may treat the child differently from others. Children may not be comfortable in accepting their new brother or sister obtained through surrogacy. All intended parents might be confused whether to tell the child about its birth, fearing that hearing the truth may distress the child. At the age of 18 the child will have the right to discover identity of its genetic parents. And hence the intended parents have the fear of loosing them.
Surrogate child
A child who is born through surrogacy is called surrogate child. This child will have more than two parent couple & bit complicated.
- The intended parents who adopt the child for rest of its life.
- Surrogate mother & her husband.
- Woman who donated the egg for surrogacy (genetic mother) & her husband if any.
- Man who donated the sperm for surrogacy (genetic father) & his wife if any.
Precautions
The surrogate mothers, intended parents as well as donors must take proper precautions. Medical examination should be conducted before using their eggs, sperms or even a womb to ensure that no infection or any genetically transmissible diseases are present with all those persons who are going to be involved in surrogacy process.
Legal conditions
Law does not prohibit surrogacy. But proper agreement should be made before & after getting into this decision both by the surrogate mother & the intended parents. For a child born through surrogacy, the real mother is always the carrying mother i.e., the surrogate mother .In order for the intended parents to become the legal parents; they must adopt the child by legal methods. Problems may arise if the child born is physically or mentally disabled & the intended parents change their mind, then surrogate mother is legally responsible for the child. Sometimes the motherhood of a surrogate mother may refuse to handover the child that she has carried for nine months .So proper agreement should be made priorly.
Relationship between intended parents & surrogate mother
It depends on the individual circumstances & wishes of concerned parties. Some surrogate mothers like to have the support of the intended parents throughout the pregnancy and equally the intended parents often want to share the experience and be involved with the pregnancy .Others prefer to have limited contact.
Once the child is born, in some cases the contact stops & as per the mutual agreement, the child is handed to the intended parents, except for the communication required for transferring the legal parentage of the child. In other cases the intended parents will send photographs of the child to the surrogate mothers. In some cases, the child will know the surrogate mother and her family. So everything depends on the surrogate mother and intended parents agreement on the level of contact which they feel is appropriate for them.
Conclusion
While there has been much publicity on the topic in general, there are still a lot of misconceptions about what surrogacy is and how it can be accomplished. The surrogacy process is a happy, joyful and rewarding experience that is built on mutual respect, friendship and teamwork. Surrogacy might be the only opportunity for some people to have children but it is not something that anyone should enter into lightly, people should take time to reflect on it and, if possible, discuss it with partners, family or friends before taking further step.
ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION FOR INFERTILITY
Artificial insemination (AI) has a long history and is easier technique than some other methods of assisted conception. In AI, warmed prepared sperm is introduced into the woman’s genital tract at around the time of ovulation, with the aim of getting the sperm nearer to the egg. The most common Artificial Insemination procedure, which is also called Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), is often combined with fertility drugs.
Definition
Artificial insemination is the process by which sperm is placed into the reproductive tract of a female for the purpose of impregnating the female by using means other than sexual intercourse. In humans, it is used as assisted reproductive technology, primarily to treat infertility but is also increasingly used to enable women without a male partner (i.e., single woman and lesbians) to produce children by using sperm provided by a sperm donor. The woman is the gestational and genetic mother of the child produced, and the sperm donor is the genetic or biological father of the child. Specifically, freshly ejaculated sperm, or sperm which has been frozen and thawed, is placed in the cervix (intracervical insemination) (ICI)) or in the female’s uterus (intrauterine insemination) (IUI) by artificial means.
Types of Artificial insemination
There are 2 types, namely:
- Artificial Insemination using Husband sperms : Semen (A.I.H) sample will be provided by the male partner of the woman undergoing artificial insemination. Sperm is usually obtained through masturbation or the use of an electrical stimulator, although a special condom, known as a collection condom, may be used to collect the semen during intercourse.
- Artificial insemination using Donor sperms : Semen (A.I.D) sample known as “donor sperm” provided by a known or anonymous sperm donor can be used can be used for insemination.
Indications
A.I is most commonly used for infertility associated with
- Endometriosis : Women with mild endometriosis can be treated with A.I
- Unexplained infertility: A.I. is used as the first line of assisted conception treatment for couples with “unexplained infertility”.
- Single Woman: Woman without a male partner may also want to have A.I, as using sperm donated through a Fertility Hospital has a number of advantages over self-insemination at home.
- Male factor infertility (Oligospermia): Sperm is placed directly inside the woman. IUI can help couples where the man has a low sperm count or poor motility (the ability of the sperm to move), as long as there are sufficient levels of healthy, motile sperm to make the treatment worthwhile.
- Coital Failure: IUI can also help couples who are unable to have intercourse because of disability, injury or difficulties such as premature ejaculation.
- Immunological abnormalities: Women who have allergy towards semen needed artificial insemination.
- Polycystic ovaries(PCOS): Lack of ovulation that have been stimulated with drugs to ovulate. Followed By A.I
Techniques
There are several techniques to perform artificial insemination. Following are the techniques done in our Mediwave IVF & Fertility Hospital:
- Intravaginal Insemination: When an ovum is released, semen provided by the woman’s male partner, or by a sperm donor is inserted into the woman’s vagina. The semen may be fresh or it may be frozen semen which has been thawed. Where donor sperm is supplied by a sperm bank, it will always be quarantined and frozen and will need to be thawed before use. In the case of vaginal artificial insemination, semen is usually placed in the vagina by way of a needle less syringe.
- Artificial insemination using Sharath Canula : A longer tube, known as a ‘Sharath Canula’ may be used to facilitate deposit of the semen deeper into the vagina. The woman is generally advised to lie still for a half hour or so after the insemination to prevent seepage and to allow fertilization to take place.
- Cervical Cap : A specially designed cervical cap, a conception device, which holds the semen in place for a period of time, usually for several hours, to allow fertilization to take place. Using this method, a woman may go about her usual activities while the cervical cap holds the semen in the vagina.
- Intracervical Insemination (ICI) : The easiest way to inseminate, where semen is injected high into the cervix with a needle-less syringe. This process most closely replicates the way in which semen is deposited by the penis in the cervix or fornix when the male ejaculates during vaginal intercourse. It is the simplest method of artificial insemination and ‘unwashed’ or raw semen may be used. It is probably therefore, the most popular method and is used in most home, self and practitoner inseminations, However, more technical procedures may be used which increase the chances of conception.
- Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI): Where sperm is injected directly into a woman’s uterus. ‘Washed sperm’, that is, spermatozoa which have been removed from most other components of the seminal fluids, can be injected directly into a woman’s uterus in a process called intrauterine insemination (IUI). If the semen is not washed it may elicit uterine cramping, expelling the semen and causing pain, due to content of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are also the compounds responsible for causing the myometrium to contract and expel the menses from the uterus, during menstruation.
- Intra Fallopian Insemination : Insemination may also be performed into the Fallopian tube although this procedure is no longer generally regarded as having any beneficial effect compared with IUI.
- Intra Peritoneal Insemination : Processed sperms can be directly injected into the peritoneum on the day of ovulation. Chances of ectopic pregnancy are more by this technique.
Source of Semen
- Husband : Sperm is provided by the women’s husband.
- Donor :Sperm is obtained by the donor.
- Sperm Bank :If sperm is provided by a sperm donor through a sperm bank, it will be frozen and quarantined for a particular period and the donor will be tested before and after production of the sample to ensure that he does not carry a transmissible disease. Sperm samples donated in this way are produced through masturbation by the sperm donor at the sperm bank. A chemical known as a cryoprotectant is added to the sperm to aid the freezing and thawing process. Further chemicals may be added which separate the most active sperm in the sample as well as extending or diluting the sample so that vials for a number of inseminations are produced.
Procedure
There are several procedures followed for artificial insemination. IUI is most commonly used. The procedure we follow in our hospital is as below :
- The woman usually is stimulated with medication to stimulate one or more egg development and the insemination is timed to coincide with ovulation – release of the eggs from the follicles.
- A semen specimen is either produced at home or in the office by masturbation after 2-5 days of abstinence from ejaculation.
- The semen is “washed” in the laboratory (called sperm processing or sperm washing). By this process, the sperm is separated from the other components of the semen and concentrated in a much smaller volume. Various media and techniques can be used to perform the washing and separation, depending on the specifics of the individual case and preferences of the fertility doctor and laboratory. The sperm processing takes about 20-60 minutes, depending on the technique utilized.
- A speculum is placed in the vagina and the cervical area is gently cleaned.
Then the separated and washed specimen consisting of a purified fraction of highly motile sperm is placed either in the cervix (intracervical insemination, ICI) or higher in to the uterine cavity (intrauterine insemination, IUI) using a sterile, thin and soft catheter. Intrauterine insemination has a better success rate than intracervical insemination. Therefore, it is the preferred method at the large majority of fertility specialist centers.
Stimulation for Ovulation
- Natural Cycle Insemination : No medications are used if the woman is having normal menstrual cycle & normal ovulation.
- Tablets :Tablets like Cloriphene Citrate, Letrozole, Tamoxifene can be used to stimulate the ovaries for producing ovulation.
- Injections :If tablets does not give good results, then injections such as HMG or FSH (Follicular Stimulating Hormone) can be used for stimulating the ovulation.
Timing of Ovulation
A woman’s menstrual cycle is closely observed, by tracking basal body temperature (BBT) and changes in vaginal mucous or using ovulation kits, ultrasounds or blood tests. Some women are given injection called as HCG to induce ovulation.
Detection of Ovulation
In unstimulated cycles, IUI is timed to take place at the time of natural ovulation. You may be asked to detect ovulation using an ovulation predictor kit, or your fertility doctor may track your cycle using blood and urine tests or by Ultrasound Scanning. IUI is usually done between about day 12 and day 15 of a natural menstrual cycle, but the exact day will depend on your particular cycle and when ovulation is detected.
Pregnancy Chances
Through Artificial Insemination in our hospital about 60 to 70% have achieved pregnancy after 12 cycles of insemination. Pregnancy success rate for A.I depends upon sexual factors. In our Mediwave IVF & Fertility Hospital the pregnancy success rate is also 12 to 15% per menstrual cycle.
Advantages
The Artificial Insemination can be an effective solution for men with a low sperm count or poor sperm motility, where the sperm can’t make the long journey to the egg. It’s also a useful technique for couples who have problems because the man’s sperm can’t get through the woman’s cervical mucus, perhaps because of an immune reaction. It can only work for couples where the woman has no fallopian tube blockages.
Donor sperm can be used in cases where the man is producing no sperm at all, or where a woman wants to have a baby on her own or within a same-sex relationship. In the latter case, the advantages of going to a clinic for IUI with donor sperm include proper screening of the donated sperm for infections such as HIV and hepatitis. The legal rights and responsibilities of the father if the baby is conceived using fresh sperm do not apply if frozen donated sperm is used.
Complications
The risks associated with intrauterine insemination are very low. The woman could develop an infection in the uterus and tubes from bacterial contamination that originated either in the semen sample, or through a contamination of the sterile catheter in the vagina or cervical area during the intrauterine insemination procedure. Careful cleaning of the cervix during the procedure and cautious technique so as not to contaminate the insemination catheter makes these infections a rarity.
While many couples with fertility problems think that twins or more would be a great way to start a family, the reality is that multiple pregnancies increase your risk of miscarriage and other pregnancy complications.
Number of cycles
Most pregnancies resulting from insemination using the male partner’s sperm occur in the first 3 attempts. The chances for success per month drop off after about 3 attempts and drop considerably more after about 6 unsuccessful attempts. Therefore, IUI treatment is not usually recommended for more than a maximum of about 6 cycles. If the reason for infertility is lack of ovulation (anovulation), it may be more reasonable to try several more cycles (6-12 cycles total). In today’s world, many couples with fertility problems move on to IVF treatment after 3 IUI’s. Costs of fertility treatments for women are an important factor in deciding when to move on from inseminations for many couples. The relative cost-effectiveness of artificial insemination decreases substantially after 6 failed attempts.
In vitro fertilization is the next step in treatment after inseminations – and has a much higher success rate per cycle.
Contradictions
Intrauterine insemination has very little chance of working in women that are over 40 years old. IUI has also been shown to have a reduced success rate in younger women with a significantly elevated day 3 FSH level, or other indications of significantly reduced ovarian reserve.
- Not useful for women with tubal blocks.
- Not useful for women with anovulation cycles.
- Not useful for men with very poor quality sperm.
Cost Per Cycle
Artificial insemination procedures tend to be costly due in part to the expertise required to perform them. Generally, the cost of artificial insemination in our hospital includes:
- The cost of investigation and diagnosis- about Rs 5,000 to 10,000/-(first cycle only)
- The cost of drug therapy- about Rs 500 to 2,000 per cycle.
- The cost of the AI procedure- about Rs1,300 to 1,500 per insemination.
The total cost in our centre may cost around Rs 3000 to 8000/- per cycle excluding the investigations & diagnosis which is due in the fourth cycle. The cost may go up in patients who fails to ovulate with tablets. They require costlier injections – HMG or FSH.
Failed IUI What Next
- IVF
- ICSI
- Egg Donation
- Embryo Donation
- Surrogacy
- Adaptation
Conclusion
Mediwave IVF Hospital is a dedicated fertility hospital for A.I. We work hard every day to improve the success rate to decrease the cost of treatment. Couple who have financial problem will be treated with concessional cost. Even medicines are given under discount rates.
